Chemoembolization
A Minimally Invasive Cancer Treatment
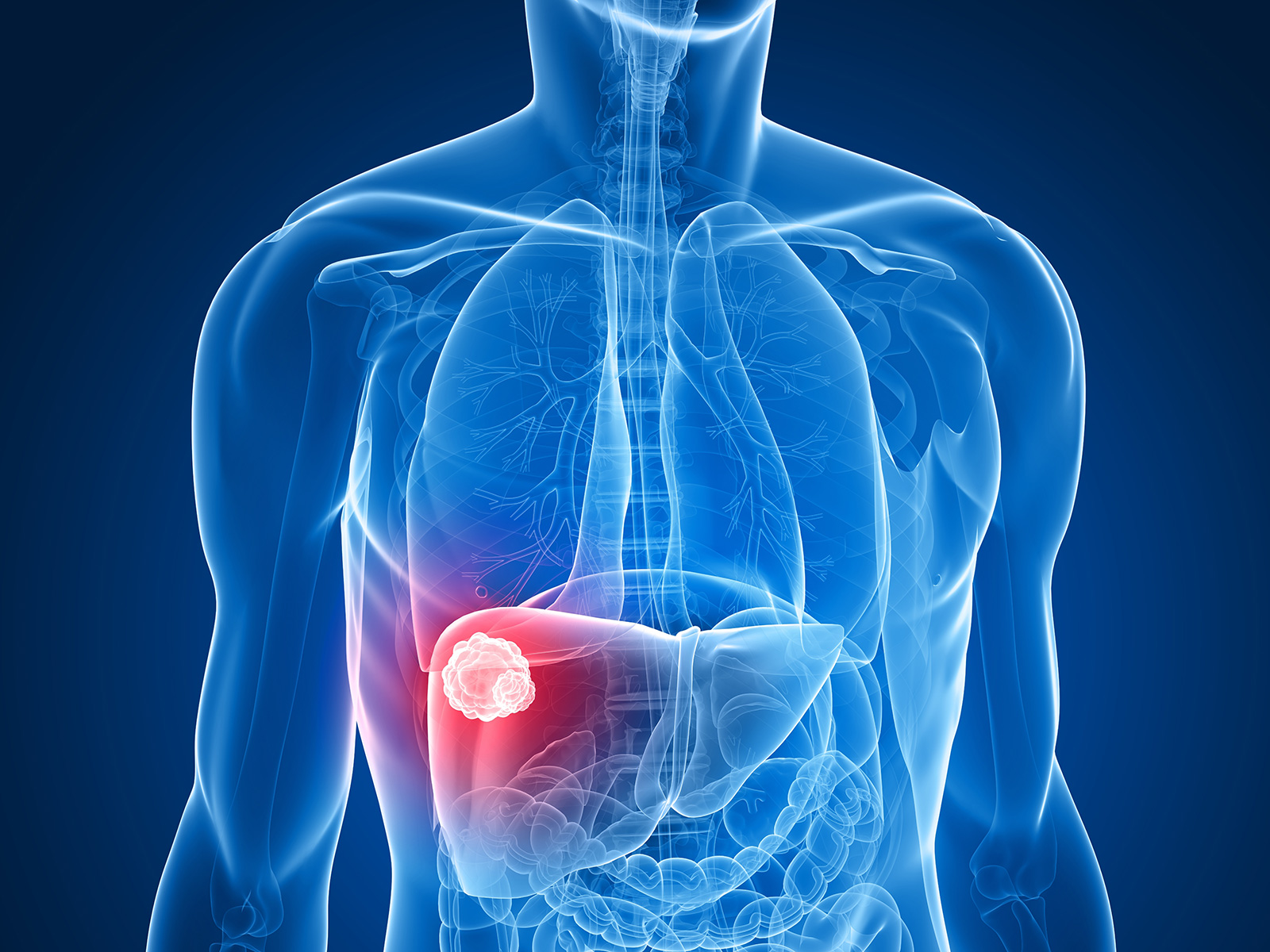
Chemoembolization is one of the many approaches to treating cancer-related issues through a minimally invasive procedure. This method of treatment is specifically designed to target and reduce the blood supply that feeds the tumor(s) commonly found within the liver.
Chemoembolization is generally used under the guidance of diagnostic imaging and can be in conjunction with other treatment options such as radiation or surgery. This advanced method assures for a more concentrated and longer effectively-active treatment process.
Chemoembolization requires the patient to go under anesthesia or moderate sedation. Through the process of Chemoembolization, a small catheter is inserted in an artery through the groin. At times, physicians may even choose to insert the catheter through the wrist. The catheter is then threaded directly into the liver artery that feeds the tumor. Small microspheres impregnated with chemotherapy drugs are injected into the catheter and directly to a specific tumor(s).
Chemoembolization’s highly concentrated approach deprives the tumors of any oxygen or nutrients while trapping in the chemotherapy micro-spheres at the site of the tumor. This procedure has proven to be highly effective in keeping the overexposure of chemotherapy drugs to healthy surrounding tissue to a minimum, while effectively treating the malignant areas of concern.
It is common for patients to report various degrees of flu-like symptoms, including nausea, pain and even a slight fever. Patients may begin to notice symptoms directly following the procedure which can last up to a few days. Such symptoms can be treated and subsided with medication.
Complications such as abscess occur in less than 3% of patients treated by Chemoembolization.
Serious complications from Chemoembolization are rare.

Have questions?
To learn more about how our physicians can help you, contact us directly (602) 200-9339